As you begin preparing for the ACT, an important early step is to get a firm grasp on the most essential ACT math topics. Armed with this knowledge, you can face down an entire test section based entirely on math and turn it from something intimidating to something you can confidently conquer!
In this ACT math topics review, we will go over 12 different ACT math question types and point you toward some winning ACT math strategies and test preparation resources. Finally, we will discuss the importance of maintaining your mental health as you enter this exciting stage of preparation. Read on to learn all about how Piqosity will be able to help you prepare for the ACT!
What are the Math Topics on the ACT?
By and large, the ACT math topics that encounter in your test prep will be concepts you have already seen before: very few ACT math questions deal with topics you learn in your senior year of high school.
The math content categories on the ACT span six math subjects:
| Math Level | Category | Percentage of ACT Math Questions |
| High School | Number & Quantity | 10-12% |
| High School | Algebra | 17-20% |
| High School | Functions | 17-20% |
| High School | Geometry | 17-20% |
| High School | Statistics and Probability | 12-15% |
| Pre-High School | Integrating Essential Skills | 20% |
You will need to know basic formulas across these topics, as you will not have a formula sheet provided. Here is a collection of key ACT math topics, showcasing example problems from within some of these categories.
Algebra Topics on the ACT Math Test
Algebra is seen on three of the ACT math subject categories: Number & Quantity, Functions, and, of course, Algebra. This makes algebraic topics a keystone subject area of your ACT test prep; together, these categories make up around 50% of the ACT math test.
1. Exponent Rules
A strong knowledge of the rules governing exponents is essential for this section.
You may be asked problems that involve simplifying expressions using one or many of the rules below:
A firm foundation of exponent rules also makes solving problems on scientific notation much easier for most students.
2. Factoring 2nd & 3rd order polynomials
You will be asked to factor 2nd and 3rd order polynomials using common algorithms such as factoring using factor trees, using the difference of squares, difference of cubes, factoring by grouping or using the quadratic formula.
An essential skill that assists with this section is a knowledge of common squares and cubes.
Example Problem:
Factor the following polynomial.
5x2 + 10y + x2y + 2y2
Solution:
There is no common factor that exists for all terms of this polynomial; y, for instance, is common for three of the terms, but it is not a factor of 5x2.However, this polynomial can still be factored through the grouping method. The grouping method requires common factors to be found for groups of terms within the polynomial.
As shown below, there is a common factor of 5 in the first 2 terms of the polynomial, and there is a common factor of y in the last two terms of the polynomial. These terms are factored out:
5(x2 + 2y) + y(x2 + 2y)
Now, notice that our factored form does have a GCF: x2 + 2y. So, we can now factor out the GCF to get:
(5 + y)(x2 + 2y)
If these two polynomials were to multiplied, the original polynomial (5x2 + 10y + x2y + 2y2) would be the resulting answer.
3. Writing & solving systems of equations using substitution and elimination
Understand how to write systems of equations from word problems, then apply either the substitution or elimination method to solve a problem.
Example Problem:
Solve the following system of equations using elimination:
y + 2x = 5
3y − x = 8
Solution:
First, we will check to see if any of the variables can be eliminated by adding the two equations together. This is not the case, so we need to manipulate one of the equations to be able to eliminate one of the variables. This can be done by multiplying the first equation by 3 to cancel out the y variable or by multiplying the second equation by 2 to cancel out the x variable.
Notice that if we multiply the second equation by 2, we will be able to directly cancel out 2x with −2x, so this is likely the easiest option: y + 2x = 5 ; 6y − 2x = 16
Now, we can add the two equations together and solve for y.
7y = 21
y = 3
We can plug this value back into either equation to solve for x.
y + 2x =5
3 + 2x = 5
2x = 2
x = 1
The solution to this system is (1, 3).
4. Linear Equations
These questions test your understanding of how to model straight lines:
Statistics and Probability on the ACT Math Test
Questions in this category will require you to analyze different methods of data collection, calculate probabilities, and more.
Example:
What is the probability of flipping a coin and landing on heads three times in a row?
Solution:
The probability of flipping a coin and landing on heads is:
Since we are trying to solve for the probability of getting heads 3 times in a row, we will need to multiply the probability of getting heads by itself 3 times.
This means that there is a 1 in 8 probability of getting heads 3 times in a row when flipping a coin.
Geometry on the ACT Math Test
1. Triangles
Understand the different properties for the 4 main types of triangles: equilateral, isosceles, right triangle, scalene.
Compute the perimeter and area of a triangle.
2. Quadrilaterals
Find the perimeter and area for different quadrilaterals such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, kites and trapezoids.
3. Circles
Find the circumference and area of circles, or slices of circles.
4. Pythagorean Theorem
Understand when to apply the Pythagorean theorem to solve problems involving triangles.
5. Coordinate Geometry
Know how to read a graph and how to find the distance and midpoint between two points on a coordinate plane.
Pre-Calculus Topics on the ACT Math Test
Pre-calculus topics are under the umbrella of Geometry when it comes to ACT math topics.
1. Trigonometry
Know how to convert between radians and degrees, as well as how to evaluate the trig. functions sin, cos and tan to specific angle measures.
2. Special right triangles
Understand the properties of the 30-60-90 and 45-45-90 special right triangles.
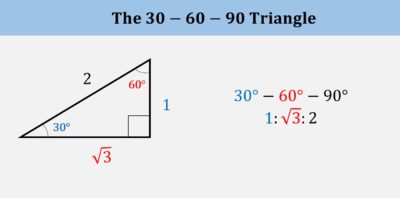
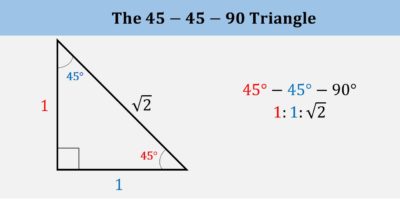
The ACT Math Test’s “Essential Skills” questions
These questions will cover the math skills students should have learned before high school.
- Order of operations
- Constant proportions
- Converting between fractions, decimals and percentages
- Simple and weighted average
Although the skills themselves are fairly straightforward, you may be asked to use them in particularly complex ways. Some atypical problems may require students to combine skills across multiple mathematical disciplines.
Modeling on ACT Math
Modeling is measured throughout all the above categories, but not as its own individual concept. Rather, your score will be determined from your answers above. Broadly speaking, modeling questions are those which ask students to use mathematical skills and concepts to explain or solve real-life problems. Frequently, modeling questions use images, figures, or diagrams.
The ACT Math Section Formatting
Wondering how ACT math questions are formatted? Most ACT math questions are self-contained, but some build off of each other into a set of questions. The best way to build familiarity with these kinds of questions is to practice them!
Work through ACT Math practice tests and you’ll soon be comfortable with anything the ACT math section has to offer:
- Enhanced 2025 ACT Practice Tests – Free & Full-Length
- Answer Explanations to the 2nd ACT 2025 Math Practice Test
- More Free ACT Official Practice Test PDFs and Answer Explanations
For more help, review practice tests and answer explanations from earlier versions of the ACT:
- 2021-2022 ACT Official Test Full Answer Explanations
- 2020 ACT Official Test Full Answer Explanations
- 2015-2018 ACT Official Test Full Answer Explanations
Additionally, you’ll likely benefit from a review of our collection of tried-and-true ACT Math Strategies.
Your Brain on (ACT) Math
In addition to encouraging you to spend the time to master all of the ACT math question types (and topics), there are two other points we’d like to cover when it comes to your brain and ACT math.
First, remember that this is a timed test. Keep in mind that calculators are allowed during the ACT math test. Having a calculator on hand to assist you can also help with both your time and your score; however, you don’t want to use too much time using a calculator in cases when you mental math or scratch work could do the math in less time. Keeping track of timing on the ACT is essential, and you can hone your testing time management abilities by taking timed ACT practice tests.
Second, we know that math can be a tough subject for many students. If math is not your strong suit, you may be dealing with a significant amount of standardized test anxiety already. Review strategies for overcoming math anxiety, and remember to gently prepare over time in the months prior to your ACT test date rather than waiting until the last minute to cram!
ACT Math Practice with Piqosity!
While it’s important to review these ACT math topics, don’t stress about them too much. You have already encountered them in your regular schooling, and you have time to prepare!
If you’re looking for affordable resources to help you on your ACT journey, prepare for the ACT online with Piqosity! Along with our full-length, online ELA and Math courses for grades 5-11, we offer full SAT, ACT, and ISEE test prep courses, each of which includes:
- 12 full-length ACT Practice tests
- Over 70 concept lessons, including tutorial videos
- Real-time Score prediction (both Composite and for each Subject)
- Interactive interface allowing teachers, tutors, or parents to assign and track student work
- Personalized study guidance with the Piqosity Virtual Tutor
- …and much more!
For the new 2025 ACT, we’ve created an enhanced ACT course that includes 12 ACT practice tests! Our free community account allows you to access to try out all of Piqosity’s features—no credit card required! When you’re ready to upgrade, Piqosity’s year-long accounts start at only $89.


